The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) healthcare sector is undergoing a fundamental paradigm shift, moving from hospital-centric models toward integrated, digitally-connected care ecosystems. By 2026, regional healthcare excellence will be measured not by physical infrastructure alone, but through seamless connectivity between data systems, medical professionals, and patients.
This transformation centers on operational excellence powered by digital integration. The ability to coordinate care across clinics, hospitals, diagnostic centers, pharmacies, insurers, and virtual platforms will determine overall healthcare outcomes, efficiency, and sustainability across the region.
GCC nations are rapidly abandoning fragmented care models in favor of longitudinal patient data as the foundation of healthcare delivery. Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), interoperable health information exchanges, AI-driven clinical decision support systems, and digital diagnostics are converging to create comprehensive patient profiles. This technological integration enables physicians to transition from reactive treatment to proactive, evidence-based, and personalized care protocols.
National platforms including Dubai’s NABIDH, Abu Dhabi’s Malaffi, and UAE-wide Riayati are already facilitating secure data exchange between public and private providers. These systems have evolved beyond pilot stages to become operational backbones of clinical infrastructure, enhancing care continuity while reducing duplication, errors, and treatment delays.
Achieving connected care at scale demands significant operational maturity beyond technological implementation. This includes workforce optimization, capacity planning, insurance integration, and digitally-enabled workflows that minimize friction throughout patient journeys.
The UAE demonstrates this operational shift through measurable progress. Dubai Health Authority reports indicate doctor numbers increased to 11,890 in 2022—a 10.2% year-on-year growth—with doctor density improving to 3.35 per 1,000 population. This expanded clinical capacity, combined with digital platforms, substantially improves specialist access and reduces waiting times.
Hospital infrastructure management has also evolved, with providers maintaining optimal bed occupancy rates of 75% to balance utilization with surge capacity readiness—a critical capability given regional population growth and rising chronic disease prevalence.
Mandatory health insurance has emerged as a crucial enabler of connected care ecosystems across the GCC. Near-universal insurance coverage in markets like the UAE has transformed healthcare access, affordability, and continuity. As systems mature, incorporating long-term residents including Golden Visa holders into comprehensive insurance frameworks will be essential for sustaining the shift from episodic treatment to preventive, value-based care.
Uniform coverage enables healthcare systems to prioritize preventive measures and chronic disease management over acute interventions, strengthening risk pooling mechanisms and improving population health outcomes. By 2026, insurance data integrated with clinical systems will play a pivotal role in driving value-based care models where outcomes rather than volumes define success.
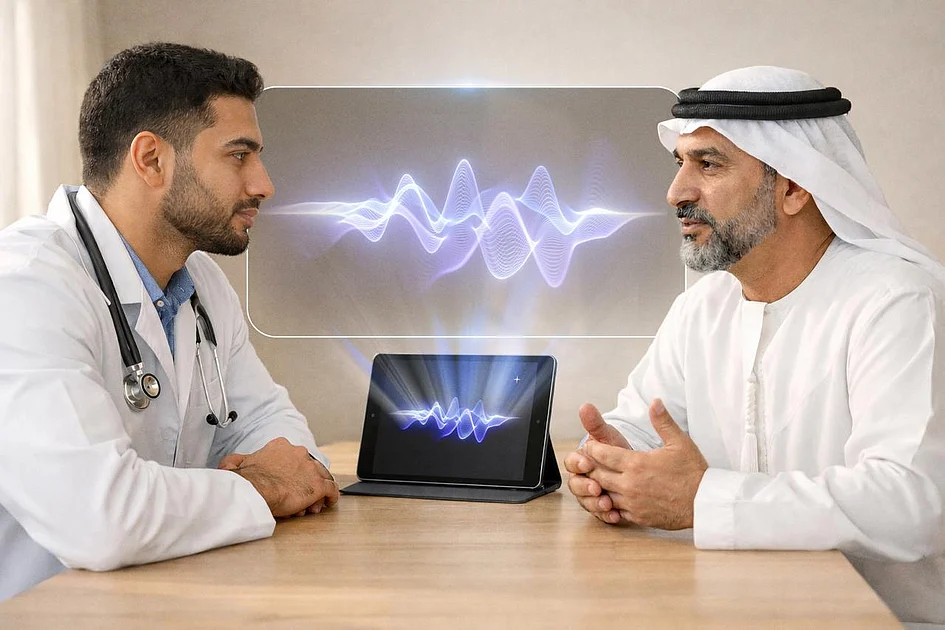
In fully connected care models, operational efficiency directly enhances patient experience. Imagine cardiac patients whose wearable devices continuously transmit vital data to physicians, seamlessly integrated into EMRs. Virtual consultations supported by AI-driven trend analysis could lead to digital prescriptions fulfilled by online pharmacies within 30-60 minutes.
This vision is already becoming reality across the UAE, supported by growing investments in telehealth, remote monitoring, AI diagnostics, and digital pharmacies. With GCC healthcare expenditure projected to grow from $109.1 billion in 2024 to $159 billion by 2029 at a 7.8% compound annual growth rate, innovation scale and pace will accelerate dramatically.
Demographic changes make this transformation imperative. The UAE’s population is projected to reach 11.1 million by 2030, with residents aged 65 and above increasing from 1.1% to 4.4%. This aging population, combined with high non-communicable disease prevalence, demands continuous, coordinated, and cost-effective healthcare models.
Connected care enables providers to manage chronic conditions more effectively, reduce hospital admissions, and support aging populations with dignity while maintaining system sustainability.
By 2026, GCC healthcare leaders will be those who have mastered the operational choreography of connected care—where data flows seamlessly, clinicians collaborate effortlessly, and patients experience care as a continuous journey rather than isolated encounters. The region, led by the UAE, possesses both the vision and infrastructure to achieve this transformation, with execution refinement, stakeholder alignment, and digital-first clinical practice embedding representing the remaining challenges.
The future of GCC healthcare will be built connection by connection rather than brick by brick—and that future is already taking shape.