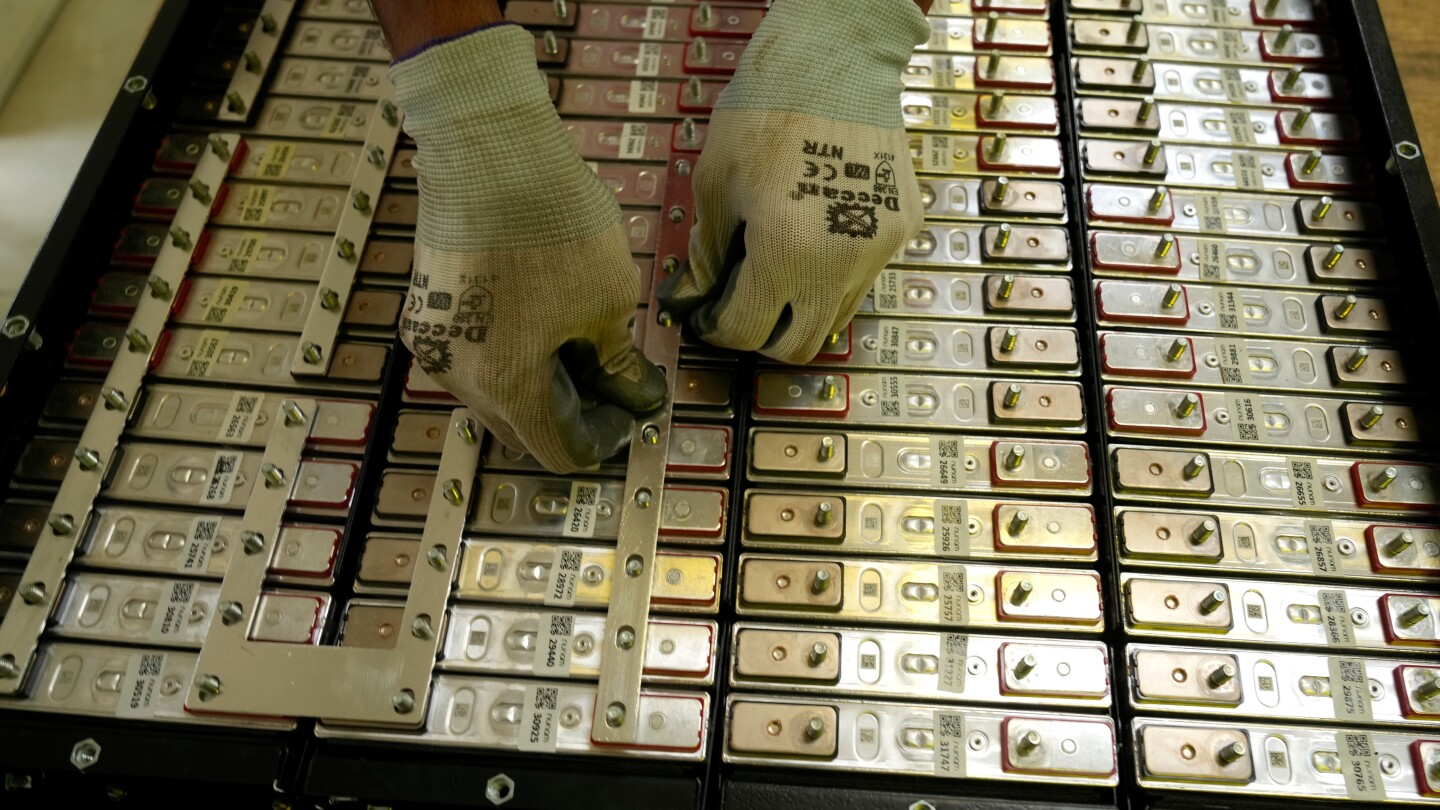
BENGALURU, India — India’s emerging battery recycling sector represents a critical frontier in the nation’s transition to clean energy, presenting both substantial opportunities and complex challenges. Over the past decade, a nascent industry has developed to extract valuable minerals—including lithium, cobalt, and nickel—from electric vehicle batteries, smartphones, and consumer electronics. These recovered materials are increasingly feeding India’s expanding electric vehicle market and solar power infrastructure, potentially reducing the country’s reliance on imported critical minerals.
According to a November study by renewable energy think tank RMI, a formalized battery recycling system could generate approximately 100,000 green jobs while satisfying nearly 40% of India’s demand for essential minerals. The report projects this recycling industry could reach a valuation of $9 billion as battery demand—primarily driven by electric vehicles—continues to surge dramatically.
Marie McNamara, RMI India program manager and report co-author, emphasizes the unique advantage of battery materials: “Unlike plastics, these materials can be recycled perpetually while maintaining their material strength and quality after refinement.”
Despite this potential, significant obstacles remain. India currently possesses 60,000 tons of battery recycling capacity, though not all is utilized due to underdeveloped supply chains connecting recovered materials to manufacturing facilities. This gap partially stems from India’s extensive informal recycling workforce, estimated at four million workers who handle various scrap materials without formal contracts or regulatory oversight.
India’s government demonstrated policy initiative by implementing battery waste management rules in 2022, mandating environmentally safe disposal practices and establishing specific collection and recycling targets for battery producers. The regulations include substantial penalties for violations but lack established outlets for discarded batteries, forcing companies to develop individual recycling systems. Energy expert Jaideep Saraswat of the Vasudha Foundation notes that while India has moved “surprisingly fast from a policy perspective,” the essential recycling supply chain remains underdeveloped.
Technical processes for battery recycling typically involve either shredding battery modules into fine powder or smelting them in industrial furnaces, followed by chemical treatment with acids to recover specific metals. Alternatively, discarded batteries can be repurposed for solar and wind energy storage after thorough testing and component cleaning. Properly executed, these processes can extract up to 90% of an EV battery’s contents.
Environmental concerns persist, however. Nishchay Chadha, CEO of U.S.-based ACE Green Recycling, warns that improper recycling can release carbon monoxide and hazardous gases, while wastewater containing heavy metals may contaminate soil and water if disposed of incorrectly. “We’ve not expanded much in India because we don’t see much appreciation for clean operations,” Chadha noted.
McNamara advocates for government-supported training programs to help informal workers transition to formal employment, emphasizing that “formalization will really help drive safety and accountability, especially considering that batteries are both defined by their toxicity as well as their potential.”
Globally, critical minerals remain dominated by China’s mining, refining, and processing operations, according to the International Energy Agency. With no operational lithium mines currently, India depends heavily on imports. Effective mineral recovery from used products could significantly address this dependency, though Chadha cautions that India should take “baby steps first,” noting that China treats recycling as an essential—if sometimes unprofitable—component of its broader supply chain strategy.
Despite challenges, industry optimism persists. Rajat Verma, founder and CEO of Lohum Cleantech, envisions substantial growth: “If the momentum that is there in India today continues, we can probably create five multibillion-dollar giants in this industry.” This sentiment reflects the broader recognition that battery recycling represents not just an environmental imperative but a strategic economic opportunity in India’s clean energy transition.