In a significant move to address the global AI skills gap, former Google AI engineer Malika Malik has launched myAIcademy, an adaptive learning platform designed to make artificial intelligence education accessible to millions worldwide by 2030. The initiative comes as AI is projected to contribute $15.7 trillion to the global economy within the decade, yet current educational offerings predominantly cater to developers, leaving professionals across consulting, law, healthcare, education, and other sectors underserved. The platform represents a paradigm shift from traditional AI education, which suffers from an 80% learner dropout rate and content that becomes outdated within six months due to the rapid evolution of AI technology. myAIcademy’s core innovation lies in its dynamic, real-time content updating system and personalized learning paths tailored to individual goals, roles, and industries. At the heart of the platform is Aimy, a voice-enabled AI tutor that provides contextual explanations, answers questions in real-time, and adapts to individual learning styles. To enhance engagement, the platform incorporates gamified elements including bite-sized lessons, hands-on AI playgrounds, progress tracking, XP points, achievement badges, and leaderboards. The founding team combines technical expertise from Google, Microsoft, and IIT with educational experience from prestigious institutions including Oxford University. Backed by investors such as Lucy Chow of the World Business Angels Investment Forum and academic advisors including Georgetown University’s Roberto Ordonez, myAIcademy will be available on iOS and Android platforms, offering lifetime access and practical solutions for individuals, enterprises, and educational institutions.
分类: technology
-

Satellite launch marks a new milestone in UAE-China cooperation
A landmark achievement in international space cooperation was realized on Wednesday as the Arab Satellite 813 successfully reached orbit aboard China’s Kinetica 1 rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. This joint project between the United Arab Emirates and China represents the first pan-Arab space collaboration initiative, with leadership from the UAE’s National Space Science and Technology Center.
The sophisticated Earth observation satellite, equipped with advanced hyperspectral and panchromatic imagers plus an atmospheric polarimeter, will deliver critical data for environmental monitoring, climate research, and detailed mapping applications. The project name commemorates the year 813 CE, marking the establishment of Baghdad’s House of Wisdom during Islam’s Golden Age of scientific advancement.
This collaboration stems from a 2023 agreement between the Shanghai Engineering Center for Microsatellites and UAE space authorities. More than 40 engineers from across Arab nations contributed to the satellite’s development, providing hands-on experience for UAE University students and researchers in space system design and testing.
The Shanghai Engineering Center for Microsatellites described the mission as establishing “a solid foundation for further strategic collaboration” between the two nations in space technology. This successful launch demonstrates growing technological partnership between China and Middle Eastern nations while advancing Arab capabilities in space science and satellite technology.
-

South Korea to become the world’s first country to enforce AI law
South Korea is poised to make regulatory history by implementing the world’s first comprehensive artificial intelligence legislation. The AI Framework Act, scheduled to take effect on January 22, 2026, establishes groundbreaking requirements for AI development and deployment while creating new governance structures for the rapidly evolving technology.
The legislation mandates the formation of a national AI committee charged with overseeing the country’s artificial intelligence strategy. This body will develop and implement a comprehensive three-year AI plan addressing safety protocols, transparency standards, and disclosure obligations for certain AI systems. The framework represents the most structured approach to AI governance yet implemented by any nation.
While the European Union previously passed AI-related legislation, its full implementation faces delays until 2027 due to industry pressure and competitive concerns. South Korea’s earlier enforcement timeline positions it as the definitive pioneer in formal AI regulation.
However, the ambitious schedule has raised significant concerns within Korea’s technology sector. Industry associations report that 98% of local AI startups lack established compliance systems for the impending regulations. A recent survey of 101 AI startups revealed that nearly half remain unfamiliar with the law’s具体要求, while another 48.5% acknowledge awareness but inadequate preparation.
Industry officials warn that the compressed timeline—with enforcement decrees expected just before the law takes effect—creates particular challenges for smaller companies and startups. Some fear services may require abrupt modification or suspension once the regulations take force.
The regulatory pressure is already influencing business decisions, with growing numbers of Korean AI startups considering expansion to markets with softer governance approaches. Japan’s voluntary compliance model has emerged as a particularly attractive alternative for companies concerned about Korea’s stringent requirements.
This pioneering legislation represents a critical test case for balancing innovation promotion with responsible AI development, potentially setting global standards for how nations approach artificial intelligence governance.
-

China’s self-developed technology advances its high-speed railways
China’s high-speed rail sector is achieving unprecedented technological milestones through fully independent innovation, demonstrating world-leading capabilities in both extreme-condition operations and record-breaking velocity. The recently inaugurated Shenyang-Baihe line in northeastern China serves as a showcase for these advancements, featuring specialized rolling stock engineered for frigid environments and intelligent operational systems.
The Fuxing CR400BF-GS Electric Multiple Unit (EMU), specifically designed for extreme cold regions, represents just one facet of China’s rail technology progression. More remarkably, manufacturing processes have achieved extraordinary precision through intelligent production methods. Track slabs for the Shenyang-Baihe line, measuring 5.6 meters by 2.5 meters, now require merely 10 minutes per unit with height variations controlled within microscopic tolerances comparable to a human hair’s thickness.
The most dramatic advancement emerges in speed technology. The CR450 bullet train, currently undergoing intensive pre-service trials, has achieved breathtaking velocity benchmarks: 453 kilometers per hour in single-train testing and a world-record relative passing speed of 896 kilometers per hour. This places China in uncharted territory as no commercial high-speed rail system globally operates above 400 km/h, eliminating existing reference models for such velocities.
Engineering such extreme performance demanded radical aerodynamic solutions. Between 350-400 km/h, resistance increases by 30%, with 95% originating from air drag. The CR450 addresses this through a lengthened streamlined nose, 20-centimeter lowered roofline, and 50-tonne weight reduction collectively achieving 22% drag reduction.
Beyond physical engineering, China has developed sophisticated control systems featuring complete intellectual property ownership. The CTCS-3 ATP and ATO system, independently developed by CRSC Research & Design Institute, enables autonomous inter-station operation, overspeed protection, and precision stopping even in low-visibility conditions.
For western regional development, a new generation train control system integrated with BeiDou satellite navigation combines multiple data sources including satellite positioning, electronic mapping, and speed sensors to enhance positioning accuracy and reliability in challenging environments.
With China’s high-speed network projected to exceed 50,000 kilometers by end-2025, these technological advances position the country at the forefront of developing not just extensive but intelligent, resilient future-ready rail infrastructure.
-

Nvidia invests $2 billion in chip design software maker Synopsys
In a landmark strategic move reinforcing its artificial intelligence market leadership, Nvidia has announced a substantial $2 billion investment in semiconductor design software pioneer Synopsys. This investment forms the cornerstone of an expanded multi-year partnership aimed at developing next-generation AI-powered tools for advanced product design across multiple industries.
The collaboration, formally unveiled on Monday, represents Nvidia’s latest strategic maneuver in a series of calculated investments designed to solidify its dominance within the rapidly expanding AI ecosystem. This partnership specifically targets transitioning high-tech industries from traditional central processing units toward Nvidia’s specialized graphics processing unit architecture.
Synopsys’s sophisticated software platform serves as an industry standard for designing complex systems ranging from cutting-edge computer chips to advanced aerospace components. Engineering teams globally utilize these tools to conduct comprehensive virtual simulations before proceeding to physical prototyping—a process that typically requires weeks of computational analysis.
During a joint press conference, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang emphasized the transformative potential of this collaboration: “The order of magnitude speed-up achieved through our combined technologies will unlock opportunities that have never been possible before. We’re essentially redefining the boundaries of computational design.”
Significantly, both companies clarified that the partnership remains non-exclusive, with Synopsys CEO Sassine Ghazi confirming ongoing collaborations with other chip manufacturers including AMD and Intel. The $2 billion investment specifically involves Nvidia’s acquisition of Synopsys common stock at $414.79 per share, representing a modest 0.8% discount to Friday’s closing price.
Market response proved positive following the announcement, with Synopsys shares climbing nearly 5% while Nvidia registered a 1.4% gain. This investment continues Nvidia’s aggressive deployment of capital within AI-adjacent sectors, following previous strategic positions in industry leaders including OpenAI and Anthropic.
-

New rocket set to debut soon, launch six satellites
Chinese commercial space company Galactic Energy is poised to launch its new-generation Ceres-2 solid-propellant carrier rocket on its inaugural mission within days, according to industry sources. The launch operation will be conducted from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, marking a significant milestone for China’s private aerospace sector.
The maiden flight will serve dual purposes: validating the rocket’s overall design and performance capabilities while deploying six commercial satellites and two experimental payloads with a combined mass exceeding one metric ton. The Ceres-2 represents a substantial advancement in China’s commercial launch vehicle technology, featuring a three-stage solid-propellant core complemented by a liquid-fueled upper stage.
With a total weight of 100 tons, the new rocket demonstrates impressive payload capacity, capable of delivering 1.6 tons to low-Earth orbit (500 km altitude) or 1.3 tons to sun-synchronous orbit (500 km altitude). The manufacturer highlights its exceptional carrying efficiency and operational flexibility, supporting both land-based and maritime launch platforms.
The rocket’s development involved manufacturing and functional testing across multiple facilities in Ziyang, Sichuan Province and Haiyang, Shandong Province. Galactic Energy ranks among China’s pioneering private enterprises achieving orbital capability with indigenous rocket technology. The company’s leadership team brings extensive experience from state-owned aerospace giants including China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation.
This launch continues the success trajectory established by Galactic Energy’s Ceres-1 model, which completed its debut flight in November 2020. The earlier variant has achieved 20 successful orbital missions out of 22 attempts, deploying 85 commercial satellites to date. The Ceres-1 stands at 20 meters with 1.4-meter diameter, capable of delivering 300kg payloads to sun-synchronous orbit.
The Ceres-2 debut coincides with increased activity among Chinese commercial rocket developers, with LandSpace recently introducing its ZQ-3 model and Space Pioneer preparing its TL-3 rocket for imminent first flight, signaling robust competition and innovation within China’s burgeoning private space industry.
-

China aims for twin-track use of Nvidia H200 amid back door fears
China is demonstrating a notable shift in its position regarding Nvidia’s H200 graphics processing units (GPUs), moving from initial skepticism to a pragmatic governance strategy. This strategic recalibration follows the Trump administration’s December 8 announcement permitting Nvidia to export H200 products to China under specific national security conditions, a decision reportedly communicated directly to Chinese President Xi Jinping during a November 24 phone conversation.
The initial Chinese response to potential H200 exports, characterized by warnings of ‘sugar-coated bullets’ that might undermine domestic chip development, has evolved into a more nuanced ‘twin track’ approach. This strategy allows Chinese firms to utilize H200 chips for AI model training—which demands high-performance processing capabilities—while employing domestic chips for inference tasks requiring less computational power but greater energy efficiency.
Chinese technology giants including ByteDance and Alibaba have expressed significant interest in acquiring H200 chips, with industry sources indicating potential orders approaching 100,000 units. The appeal lies not only in the H200’s substantial performance advantage over previous options but also in Nvidia’s deeply entrenched CUDA ecosystem, which offers a comprehensive development environment that domestic alternatives cannot yet replicate.
Despite this openness to foreign technology, Chinese commentators emphasize the continued importance of developing domestic capabilities. Columnist Tangyipao notes that while the H200 can help alleviate computing power bottlenecks, China must remain vigilant against technological lock-in and continue advancing its indigenous chip industry, particularly through products like Huawei’s Ascend processors.
Security concerns regarding potential ‘back doors’ in Nvidia’s technology have been partially addressed through the company’s December 10 announcement of a software-based monitoring tool designed for GPU management rather than control. Nvidia explicitly stated its chips contain no hardware tracking technology, kill switches, or back doors—though some Chinese analysts call for independent verification of these claims.
This balanced approach reflects China’s historical development philosophy of ‘walking on two legs,’ advocating for simultaneous advancement across multiple sectors without becoming overly dependent on any single technology or approach.
-
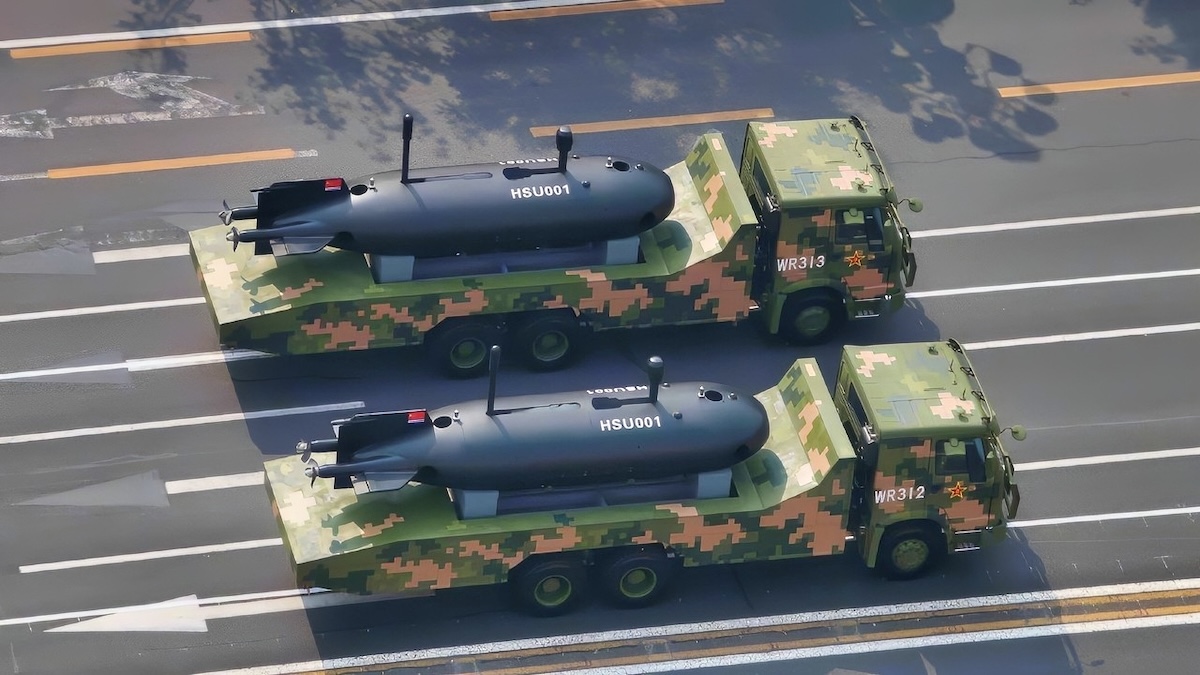

PLAN’s big underwater drones push undersea power toward US shores
China’s testing of colossal uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) represents a transformative development in maritime warfare with far-reaching implications for global security. Recent reports indicate Beijing is conducting secret trials of two distinct extra-extra-large UUV (XXLUUV) models in the South China Sea, with these systems comparable in size to conventional submarines.
According to naval analysts, these diesel-electric powered drones possess operational ranges exceeding 18,500 kilometers and can carry diverse payloads including torpedoes, sea mines, and smaller underwater vehicles. Their design incorporates advanced battery banks and diesel generators, enabling extended submerged transit capabilities that could potentially bypass existing anti-submarine defenses across the Pacific theater.
The strategic implications are profound. These autonomous systems could execute minelaying operations, port blockades, or critical infrastructure attacks at unprecedented ranges. Particularly vulnerable are undersea communications cables, with Taiwan’s 24 internet cables representing a primary target that could paralyze the island’s banking, emergency services, and critical infrastructure during potential conflict scenarios.
Beyond Taiwan, the Trans-Pacific Cable network connecting Japan, Guam, and Hawaii faces similar vulnerabilities. The modular nature of these XXLUUVs allows for specialized equipment, including cable-cutting tools capable of operating at 4,000-meter depths using diamond-coated grinding technology.
Additionally, these systems threaten US underwater sensor networks like the ‘Fish Hook’ array designed to detect Chinese submarine movements through the First Island Chain. Neutralizing these sensors would enable Chinese naval forces greater freedom of movement into the open Pacific.
The Indian Ocean represents another strategic theater where these drones could operate, potentially securing China’s sea lines of communication and supporting alternative trade routes bypassing the vulnerable Malacca Strait. This expansion could bring China into direct competition with India and other regional powers.
While theoretically capable of nuclear delivery missions similar to Russia’s Poseidon system, analysts question the strategic value of such applications given their slow transit times compared to ballistic missiles. China’s existing nuclear arsenal, including DF-41 ICBMs capable of reaching the US mainland in approximately 30 minutes, provides more credible deterrent options.
The scale of production and existence of competing designs suggest these are not mere research projects but part of a serious procurement program that could fundamentally alter the strategic balance across the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
-
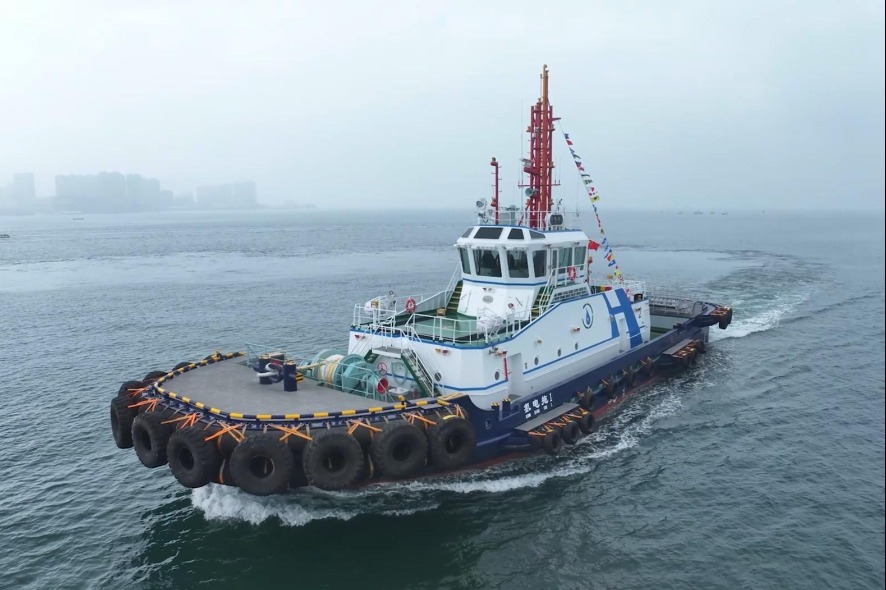

Qingdao Port integrates clean energy with China’s first hydrogen-electric tugboat
Qingdao Port in Shandong Province has launched a groundbreaking clean energy initiative with the commissioning of China’s first hydrogen-electric hybrid tugboat, marking a significant advancement in sustainable maritime operations. Since its mid-summer deployment, the innovative vessel has been actively supporting port operations while demonstrating substantial environmental benefits.
According to Captain Zhou Zixiang, the tugboat features an advanced hybrid propulsion system integrating hydrogen fuel cells with liquid-cooled lithium battery technology. This configuration enables approximately 12 hours of continuous operation on a single charging cycle. The vessel represents a technological leap forward in port machinery, offering superior energy utilization efficiency and enhanced maneuverability compared to conventional diesel-powered tugboats.
The environmental impact is particularly noteworthy, with projections indicating an annual reduction of approximately 1,500 tons of carbon dioxide emissions from this single vessel alone. The tugboat incorporates China’s Beidou Navigation Satellite System for precise positioning and operations, complemented by an intelligent shore-based charging infrastructure specifically designed for hydrogen and electric vessels.
This maritime innovation forms part of Qingdao Port’s broader green transformation strategy. Despite handling a record annual cargo throughput exceeding 700 million tons, the port has aggressively integrated renewable energy sources throughout its operations. The facility has established comprehensive solar and wind power generation systems combined with large-scale energy storage solutions, creating an integrated charging zone dedicated to clean energy vehicles and equipment.
Current statistics reveal impressive sustainability metrics: photovoltaic installations generate approximately 25 million kilowatt-hours of electricity annually, nearly 80% of operational vehicles within the port now utilize new energy sources, and clean energy accounts for 69% of the port’s total energy consumption. These collective efforts are reducing carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 20,000 tons each year, positioning Qingdao Port as a leader in environmentally responsible port management and sustainable shipping technology.
-
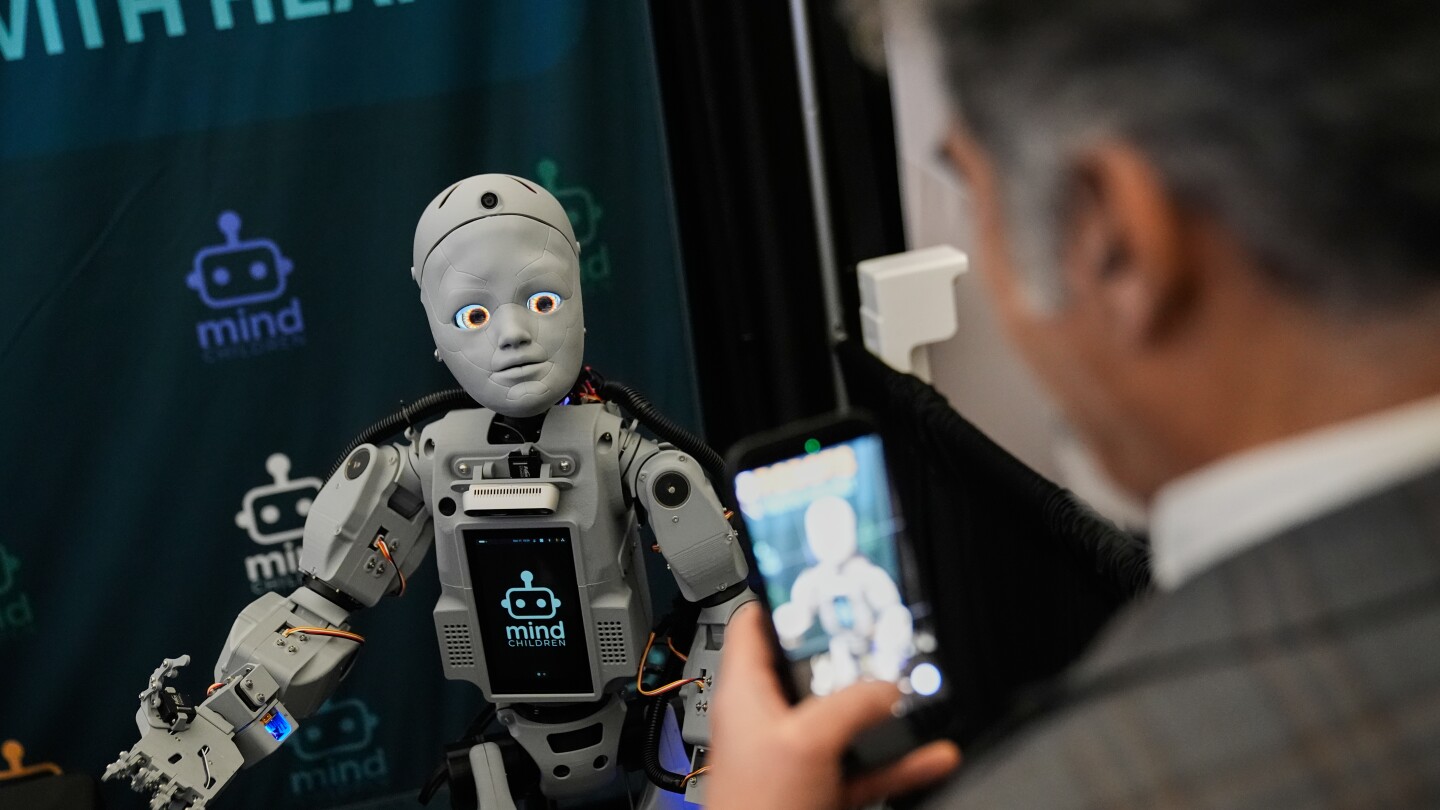
Humanoid robots take center stage at Silicon Valley summit, but skepticism remains
MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif. — The robotics sector is experiencing a paradigm shift as artificial intelligence breakthroughs breathe new life into long-standing ambitions to develop humanoid machines. This emerging transformation was the focal point of the recent Humanoids Summit, where over 2,000 engineers, investors, and entrepreneurs gathered to assess the industry’s trajectory.
Venture capitalist Modar Alaoui, founder of the summit and general partner at ALM Ventures, noted that robotics had traditionally been viewed as “a bad bet for Silicon Valley investors — too complicated, capital-intensive and boring.” However, the commercial AI boom has fundamentally altered this perception, with many researchers now believing physical embodiments of AI “are going to become the norm.”
The conference revealed both remarkable progress and significant challenges. Disney showcased its walking robotic version of “Frozen” character Olaf, scheduled to autonomously navigate Disneyland theme parks in Hong Kong and Paris by early 2025. Yet despite such entertainment applications, experts agree that truly “general purpose” robots capable of functioning as productive workplace or household members remain years away.
Substantial skepticism persists even within the industry. Cosima du Pasquier, founder of Haptica Robotics, emphasized that “the humanoid space has a very, very big hill to climb” regarding research requirements. Robotics pioneer Rodney Brooks, who did not attend, has publicly questioned whether current investments will yield dexterous humanoids despite billions in funding.
Geopolitical dimensions are emerging prominently. McKinsey & Company research identifies approximately 50 companies worldwide that have raised minimum $100 million for humanoid development, with China leading through approximately 20 initiatives compared to 15 in North America. Government incentives, component production support, and a mandated 2025 ecosystem establishment deadline contribute to China’s current momentum.
Technical advances in generative AI have provided dual stimulation: investor excitement has flooded into hardware startups, while language model breakthroughs have enhanced robots’ task-learning capabilities through visual-language training systems.
Notably absent from discussions was Tesla’s Optimus project, despite Elon Musk’s previous predictions of market availability within three to five years. The industry instead appears focused on incremental progress, drawing parallels to autonomous vehicle development timelines.
Practical implementations are already underway. Agility Robotics announced deployment of its warehouse robot Digit at a Texas distribution facility operated by Mercado Libre, while industrial robots continue to demonstrate superior efficiency in manufacturing contexts.
As the industry advances, calls for strategic national approaches are growing. Jeff Burnstein, president of the Association for Advancing Automation, is lobbying for enhanced U.S. robotics strategy, acknowledging China’s current momentum while emphasizing America’s underlying AI and technological strengths.
The consensus suggests that while humanoid robotics has entered an accelerated development phase, the path to widespread adoption remains complex and uncertain, requiring continued innovation across multiple technological domains.
