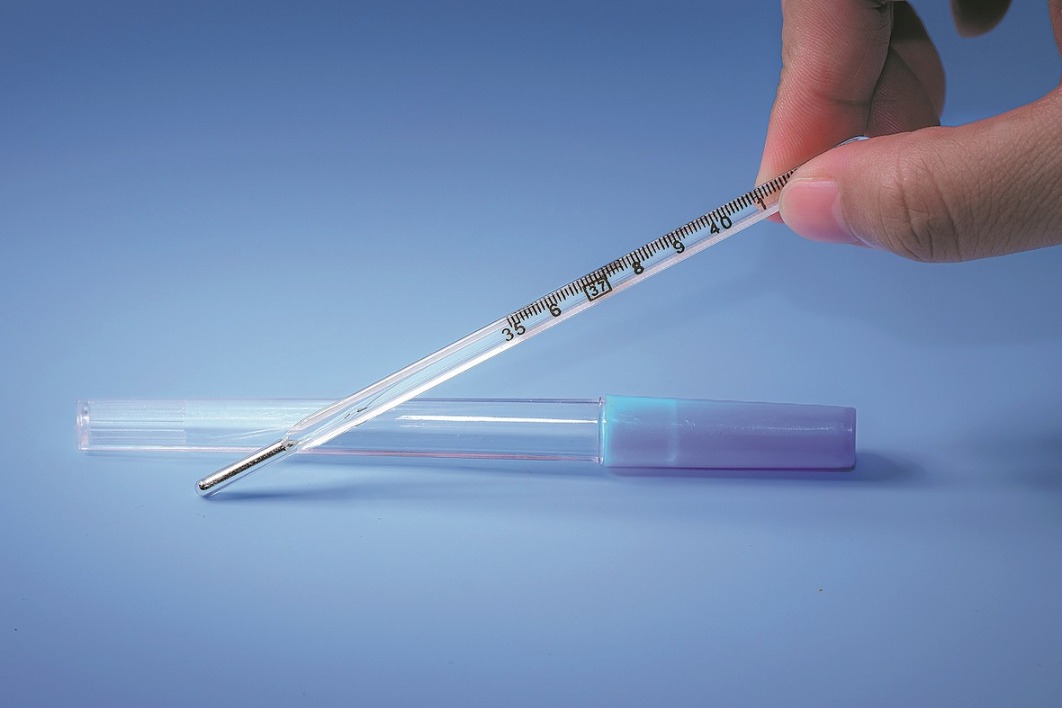
China will enforce a comprehensive prohibition on mercury-containing thermometers and blood pressure monitoring devices effective January 1, 2026, marking a significant milestone in the nation’s environmental and public health protection efforts. The ban implements a 2017 interagency directive designed to fulfill China’s commitments under the Minamata Convention on Mercury, an international treaty ratified to safeguard human health and ecosystems from mercury’s detrimental effects.
For generations, mercury thermometers have been ubiquitous in Chinese households due to their cost-effectiveness, operational simplicity, and reliable performance across diverse environmental conditions. However, each device contains approximately one gram of mercury—a potent neurotoxin classified by the World Health Organization among the top ten chemicals of major public health concern. The fragile glass construction of these instruments creates substantial spill risks, with evaporated mercury vapor posing severe threats to neurological, digestive, and immune systems through inhalation or dermal exposure.
Health authorities emphasize that proper spill management can mitigate immediate dangers. Recommended protocols include immediate ventilation of affected areas, careful collection of mercury beads using stiff paper or cardboard, and proper disposal at designated hazardous waste facilities. Crucially, vacuum cleaners or brooms should never be employed as they disperse toxic particles and amplify exposure risks.
Medical experts affirm that advanced alternatives offer safer and equally effective solutions. Dr. Li Tongzeng of Beijing Youan Hospital’s infectious disease department confirms that infrared forehead thermometers and tympanic (ear) thermometers provide accurate readings when used according to manufacturer guidelines. For traditional measurement preferences, mercury-free devices utilizing gallium-indium-tin alloys deliver precise temperature assessment without toxic hazards.
This regulatory shift represents China’s proactive approach to transforming environmental challenges into public health opportunities, aligning global treaty obligations with domestic health protection initiatives while promoting technological innovation in medical devices.