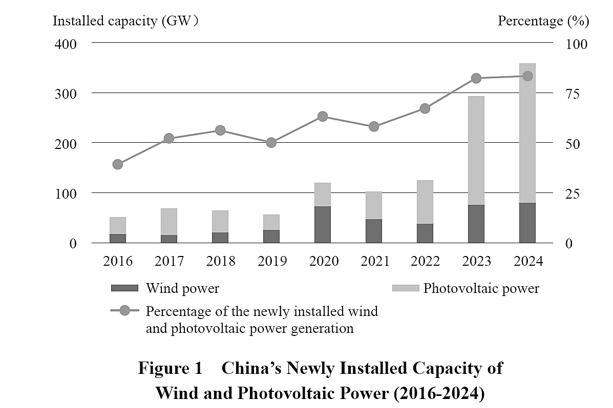
China has solidified its commitment to achieving carbon peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060, positioning itself as a global leader in climate action. The country has implemented a robust ‘1+N’ policy framework, which includes a top-level design and sector-specific action plans to guide its green transition. This framework emphasizes the development of renewable energy, energy efficiency, and low-carbon technologies, while also addressing key sectors such as industry, transport, and urban development. China has made significant strides in renewable energy, boasting the world’s largest installed capacity of wind and solar power, and leading in the adoption of new energy vehicles. The nation has also prioritized international cooperation, actively participating in global climate governance and supporting the Paris Agreement. Through these efforts, China aims to not only reduce its carbon footprint but also contribute to global sustainability and the fight against climate change.